Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is located in the southern hemisphere and is bounded by two major bodies of water: the Indian Ocean to the west and the South Pacific Ocean to the east. As the world's sixth largest country, Australia covers a total area of about 7,741,220 km 2 (around 2.99 million mi 2 ). It is continental, in that the country entirely occupies the continent it resides on.
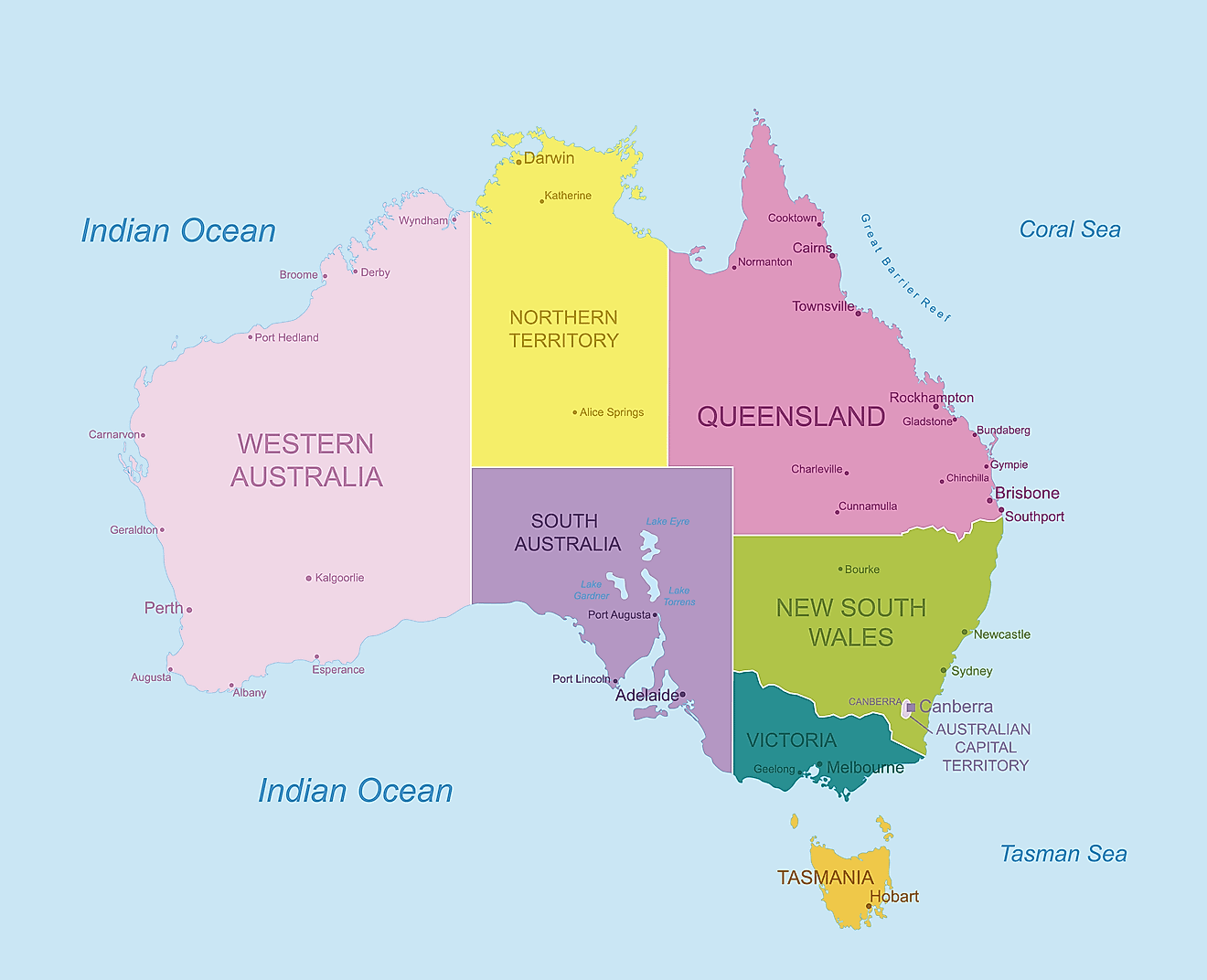
Australian geography is synonymous with vast coastal lowlands, extensive deserts, and sizable mountain ranges. It comprises six states — New South Wales, Queensland, South Australia, Tasmania, Victoria, and Western Australia — and two major mainland territories: the Australian Capital Territory and the Northern Territory. The country does not share land borders with any other nation. Instead, it lies relatively close to Indonesia, East Timor, and Papua New Guinea to the north, the Solomon Islands, Vanuatu, and the French dependency of New Caledonia to the east, and New Zealand to the southeast. Furthermore, Australia's mainland is divisible into three principal physiographic divisions: the Eastern Highlands, the Central Lowlands, and the Western Plateau.
The Great Dividing Range: The Eastern Highlands, often referred to as the Great Dividing Range, run parallel to the east coast of Australia, from the northeastern tip of Queensland, through New South Wales, and into the central part of Victoria. The highest point in Australia, Mount Kosciuszko, at 2,228 m (7,310 ft) is found in this range.
The Central Lowlands, lying between the Eastern Highlands and the Western Plateau, primarily consist of the Murray-Darling Basin, Australia's most significant agricultural area, and the Great Artesian Basin. The Murray River, Australia's longest at 2,508 kilometers (1,558 miles), runs through this region, playing a pivotal role in agriculture and water supply.
The Western Plateau, covering almost 70% of the country's landmass, includes the expansive deserts such as the Great Victoria Desert, the Gibson Desert, and the Simpson Desert. This region is characterized by flat landscapes, low relief, and abundant mineral resources, including immense deposits of iron ore and gold.
Islands: Australia is a nation of islands with over 8,000 in its territory. The largest is Tasmania, located 240 km (149 mi) to the south of the eastern part of the mainland, covering an area of about 68,401 km 2 (26,410 mi 2 ). Other notable islands include Fraser Island, the world's largest sand island, and Kangaroo Island, renowned for its diverse wildlife.
The country's marine geography is equally important, with the Great Barrier Reef spanning the northeast coast of Queensland. This world's largest coral reef system stretches over 2,300 km (1,429 mi) and is home to thousands of species of marine life like fish, whales, dolphins and six of the world's seven species of marine turtle.

Australia (officially, the Commonwealth of Australia) is divided into 6 states and 2 major mainland territories. In alphabetical order, the states are: New South Wales, Queensland, South Australia, Tasmania, Victoria and Western Australia. The two major mainland territories are: Australian Capital Territory and Northern Territory. In addition to these, there are seven external territories – Ashmore and Cartier Islands, the Australian Antarctic Territory, Christmas Island, the Cocos (Keeling) Islands, the Coral Sea Islands, Heard Island and McDonald Islands and Norfolk Islands.
Located in the northern edge of the Australian Capital Territory, in the southeastern part of the country is, Canberra – the capital of the Federation of Australia. It is also the country’s largest inland city and serves as the central administrative center of the federation. Situated on the country’s southeastern coast is, Sydney – the largest and the most populous city of Australia and Oceania. Its strategic location and magnificent harbor, makes it one of the chief ports in South Pacific. Melbourne is Australia’s 2 nd largest city.
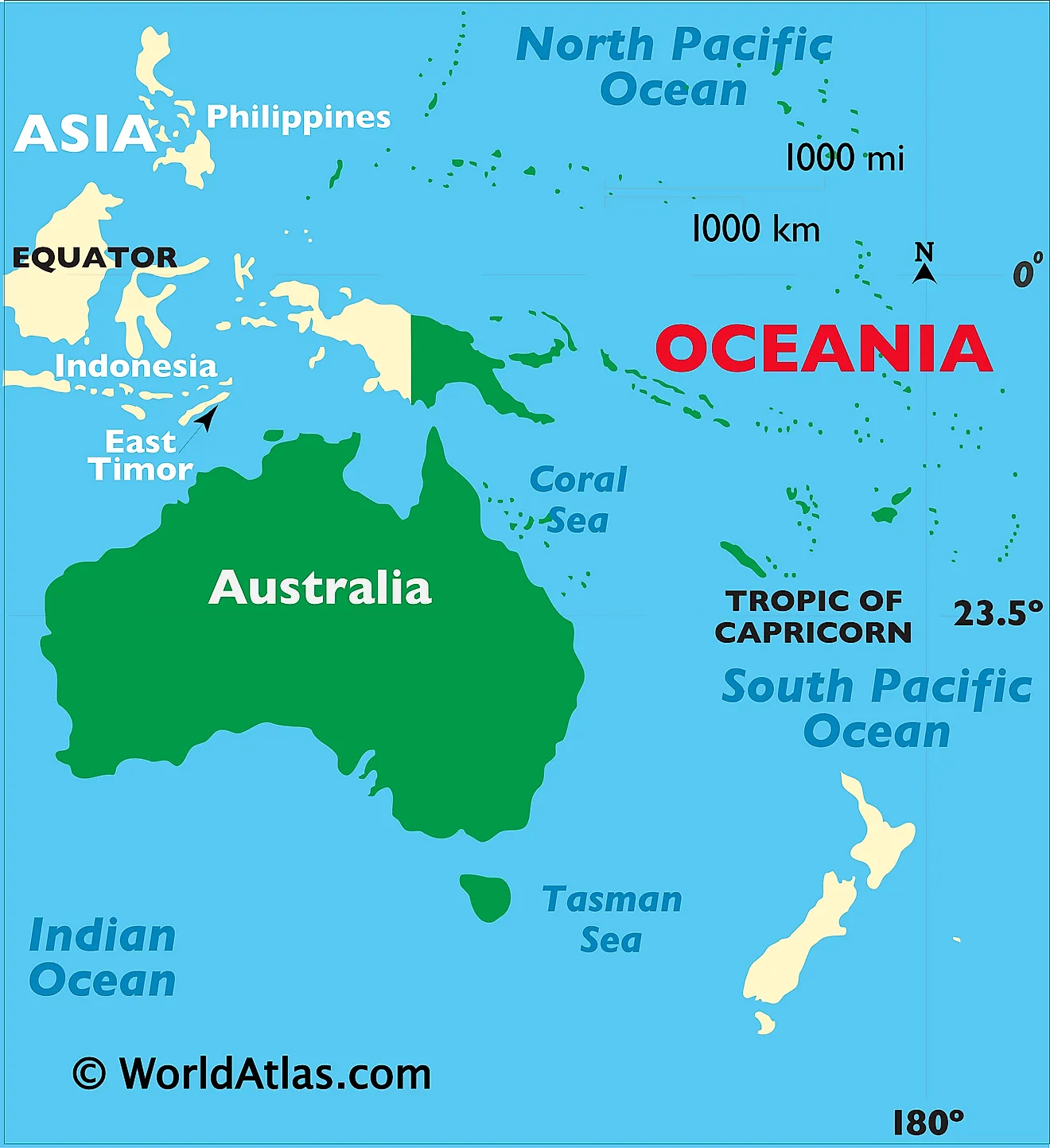
Australia is the smallest continent and the largest country in Oceania located between the Indian Ocean and Pacific Ocean in the Southern hemisphere. Australia is geographically positioned both in the Southern and Eastern hemispheres of the Earth. It is completely surrounded by the Indian and Pacific Oceans and a series of bays, gulfs, seas and straits and is situated to the south of Maritime Southeast Asia and to the north of the Antactic. Australia is separated from Papua New Guinea by the Coral Sea and Torres Strait to the northeast; from Indonesia by the Timor and Arafura seas to the northwest; from Coral Sea Islands Territory by the Great Barrier Reef; from New Zealand by Tasman Sea to the southeast; and from Antarctica by Indian Ocean to the south.
Regional Maps: Map of Oceania
This page was last updated on January 16, 2024